All age groups are susceptible to ear infections, but children are more likely to get them than adults. There is no preference based on gender. Antibiotics and analgesics can be prescribed by a general practitioner to treat mild cases of infection. Sometimes the infection can become severe and lead to potentially dangerous complications that require consultation with a specialist. Common cold episodes are typically followed by ear infections.
However, certain factors and habits can predispose to repeated ear infection, these include, frequent cough/cold, constant nasal blockage, habitual use of earbuds, cleaning ear with any sharp objects or chemicals, trauma to the ear, swimming etc.,
It is necessary to consult your ENT specialist if the ear infection persists beyond 7 days. Your ENT specialist will find out whether it is a bacterial infection or the fungal infection and prescribe you the appropriate medications. Also, your ENT specialist will diagnose from which site of the ear the infection is arising (external ear canal or the middle ear compartment), and whether it is a mild infection, dangerous infection associated with the complications.
Causes of ear infections –
Ear infection can occur due to a wide variety of reasons. Check out some of them listed here –
- Blockage on the Eustachian tubes
- Repeated ear picking and ear bud use.
- Untreated Colds
- Chronic Allergic rhinitis
- Sinus infections
- Diabetes
- Smoking
Risk factors involved in ear infections.
There are numerous risk factors that play a vital role in ear infections. These include –
- Season: Winter and fall are the two seasons where the rate of ear infections is much more. Moreover, during this time, seasonal allergies also increase due to high pollen counts.
- Age: Children under two eyes are more vulnerable to ear infections than adults. It is mainly due to the size of the Eustachian tubes.
- Cleft palate: Muscles and bone structure due to the cleft palate may enhance the risk of infection.
- Smoking: Smoking can lead to eustachian tube dysfunction and increase the chances of ear infections.
Symptoms/Signs and treatment of ear infection –
The symptoms/ signs and treatment of the ear infection depends on the part of the ear which has got infected and on the causative organism (bacterial vs fungal) causing the infection. Thus, they are classified into – the pinna infection, the outer or external ear infection, the middle ear infection, or the inner ear infection.
Pinna is the outermost part of the ear. Pinna infections are rare. Most of these infections are secondary to the trauma. It is mostly seen in boxers, wrestlers, and other sports/domestic injuries. At times pinna can get injured with a simple slap, twisting pinna or domestic fall. The minor blood vessels in the pinna rupture due to the trauma and blood accumulates between the pinna cartilage and the skin forming a hematoma. The hematoma may get infected secondarily with the bacteria and destroy the pinna cartilage.
Symptoms of Pinna or Auricular Infections –
- Visible swelling over the pinna
- Pain over the affected part if it has got infected.
- Discoloration of the skin over the affected part
- Pinna disfigurement in long standing cases
Treatment Pinna or Auricular Infections – most of the pinna infections are treated with oral antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and pain killers. When the hematoma is large and infected it may require surgical drainage with ear dressing to prevent the damage to the ear cartilage.
External ear is the part of ear extending form the outer opening of ear canals up to the eardrum or the tympanic membrane. The infection in this part is called Otitis Externa. The common cause of infection in the ear are fungal infections and bacterial infections. These are most often seen in swimmers, diabetics and use of earbuds, sharp objects, or chemicals to clean the ear wax.
Symptoms of External Ear Infections –
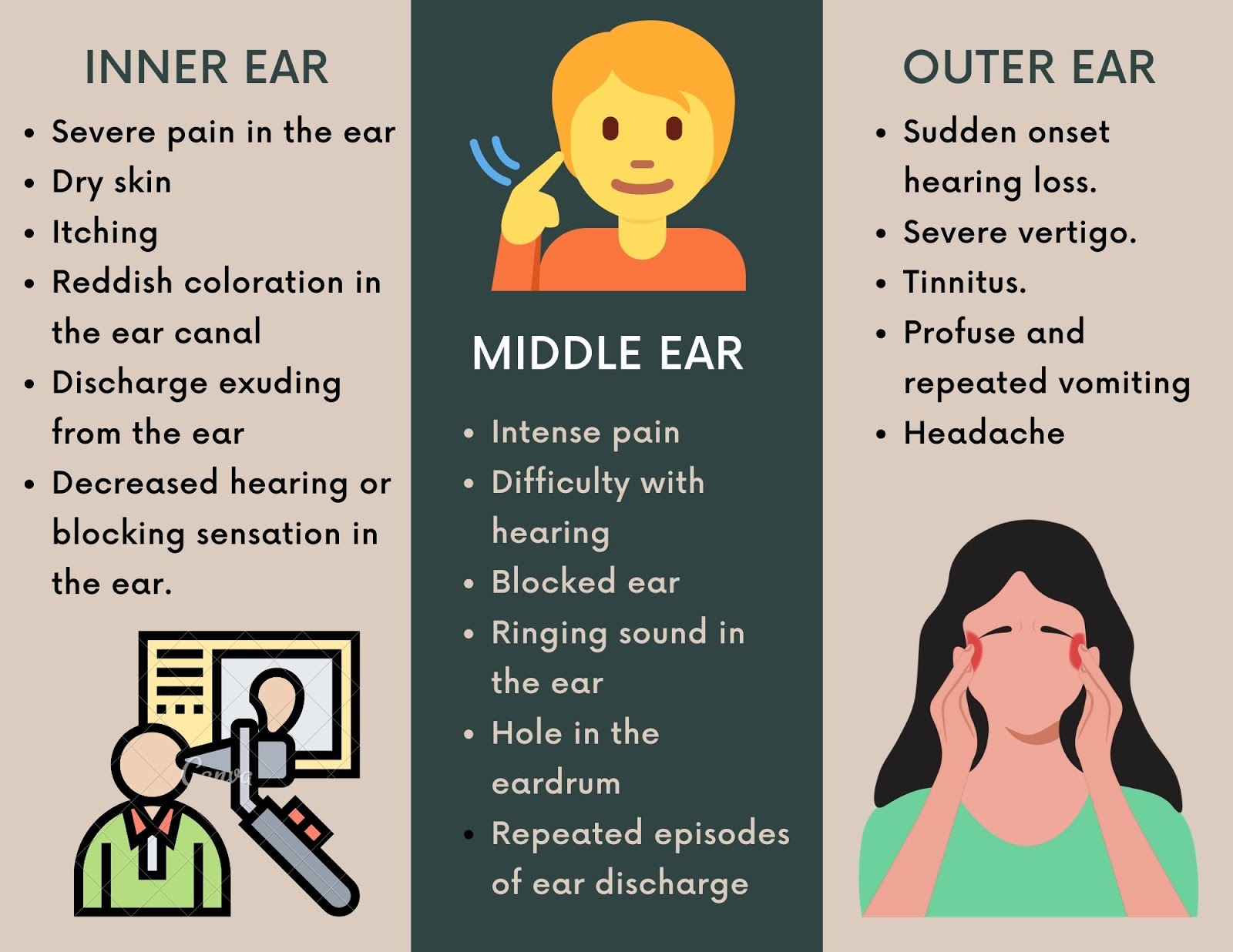
- Severe pain in the ear
- Dry skin
- Itching
- Reddish coloration in the ear canal
- Discharge exuding from the ear
- Decreased hearing or blocking sensation in the ear.
Treatment of External Ear Infections –
External ear infections are treated with oral antibiotics/pain killer medicine and antibiotic/antifungal ear drops depending on whether it is a bacterial or a fungal infection. Thorough ear cleaning of the ear canal may be required to remove the fungal debris. It is wise to seek the advice of your ENT doctor before choosing the ear drops as wrong ear drops can render the ear infection resistant to treatment and take more time to heal. Keep the ear dry as far as possible. Use shower cap while taking a bath. Avoid swimming till the infection is treated completely.
3. Middle Ear Infection
Middle ear is the part of the ear deeper to the eardrum. The infection in this part of the ear frequently follows an episode of common cold or flu. Also known as otitis media, the middle ear infection can be due to viruses or bacteria. It can be classified as acute or chronic middle ear infection based on the duration of the ear infection. Moreover, both ears can have an infection simultaneously. Thus, the symptoms are –
Symptoms of Acute middle ear infection –
- Intense pain in the initial stage which reduces after the ear discharge starts.
- Difficulty with hearing
- Blocked ear
- Ringing sound in the ear
- Fluid/ pus drainage from within the ear
- Occasionally preceding cold & fever
Symptoms of Chronic middle ear infection –
- Repeated episodes of ear discharge coinciding with the episodes of cold or flu.
- Hole or perforation in the ear drum
- Persistent decrease in the hearing
- Sticky or foul-smelling pus discharge from the ear
- Pain in the ear when there is associated fungal infection.
Treatment of Acute middle ear infection –
Acute middle ear infections are treated with oral antibiotics, oral/nasal decongestants, painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications. If pain is severed and there is impending perforation of the ear drum then your ENT may advise you for a small procedure called as myringotomy. In myringotomy a small cut is made in the eardrum to drain the pus accumulated in the middle ear. This procedure can be done under local anesthesia on a daycare basis, however in children, general anesthesia is preferred. Myringotomy is also advised for the patients who have persistent sense of ear blockage for more than 3 weeks duration despite adequate medical treatment.
Chronic middle ear infection –
Chronic middle ear infections require both medical and surgical management. While medicine is used to treat the infections, surgery is required to repair the eardrum hole, repair the damaged ossicles or to remove the diseased mastoid bone, if any. Accordingly, the surgery performed is Tympanoplasty (eardrum repair), Oculoplastic (repair of the ossicular chain- chain of very minute bones present in the middle ear which conduct the sound wave from the eardrum to the inner ear) or mastoidectomy. Any combination of these surgeries may be required depending upon the disease of the middle ear. Surgery in such cases is performed to prevent the repeated episode of ear infection and restoration of the hearing function. As a rule, earlier, the surgery performed better is the hearing outcome.
Inner ear is the innermost part of the ear. It is encased completely within the skull bone. There are two components of the inner ear, cochlea- the sensory organ for hearing and the labyrinth- sensory organ for balance. Primary inner ear infections are very rare. Inner ear infections are mostly due to viruses. Bacterial infections are uncommon and are generally seen due to spread of infection from the middle ear.
Symptoms and signs of inner ear infection –
- Sudden onset hearing loss.
- Sudden onset inability to maintain balance.
- Difficulty in walking without support.
- Severe vertigo.
- Tinnitus.
- Profuse and repeated vomiting
- Headache
- Pain in the ear or behind the ear (not common)
- Facial paralysis can be seen rarely.
Treatment inner ear infection –
Inner ear infections are medical emergencies as it can lead to permanent hearing loss or balance problems and long-lasting vertigo. It can cause troublesome tinnitus to interfere with day-to-day activities. Most of the inner ear infections are treated with antiviral medications and steroids. Steroids are necessary to reduce inner ear inflammation rapidly so that hearing and balance can be preserved. Its oral steroids are not suitable then steroid injections can be directly given inside the middle ear (intra tympanic steroid injection) These are generally well tolerated and avoid the complications of oral steroids. If bacterial infection of the inner ear is suspected, then IV antibiotics are recommended. For balance related problems specialized types of physiotherapy called vestibular rehabilitation exercises are greatly helpful. Early initiation of vestibular rehabilitation exercises helps in rapid recovery from imbalance problems. Tinnitus generally recovers with the recovery from the infection.
Preventive measures for ear infections
There are multiple preventive tips that you can follow to ensure that chance of ear infections is reduced. These are –
- Gently wipe your pinna and external ear canal with soft moist cotton cloth after bath
- Avoid use of ear buds to clean wax, they are meant for cleaning the grievances of the pinna.
- Do not attempt self-cleaning ear deep inside the ear canal- see your ENT if you have a tendency of wax accumulation.
- If water enters the ear canal, hold the hair drier at the opening of the ear canal. This will remove all the moisture without damaging the ear canal. Do not use the buds, they are harsh on your ear.
- You have frequent itching in the ear and see your ENT to get your problem diagnosed and treated properly.
- Do not ignore cold and flu. Untreated cold have higher chances of ear infections.
- Get treated for your Nasal blockage, deviated nasal septum, if any.
- If you are suffering from an allergic nasal and sinus issue, do see your ENT or allergy specialist.
- Stay away from people suffering from cold.
- For children it is important to treat the adenoid and tonsil problems promptly as these are leading causes of ear infections.
- Quit smoking.
Knowledge about the common ear infection can help you to seek timely treatment and prevent potentially dangerous complications. Hearing which is one of the important components of effective communication can be restored with treatment. Simple but important ear care tips can prevent ear infection and the subsequent complications. It is a good habit to consult your ENT on an annual basis to ensure the safety of your ears and hearing.
source: cdi

